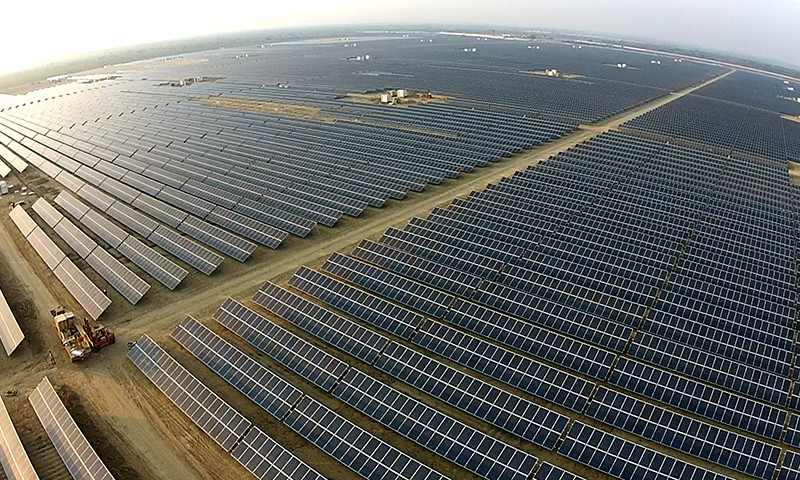
Pakistan faces a pressing challenge: balancing its growing energy demand with a reliance on expensive fossil fuels. However, a bright solution shines on the horizon – solar energy. This blog explores the compelling economic case for adopting solar solutions and delves into the different cost-effective options available.
Harnessing the Sun’s Power:
Blessed with abundant sunshine throughout the year, Pakistan presents a prime candidate for solar energy production. Solar panels directly convert sunlight into electricity, offering a clean and sustainable alternative to traditional sources.
Economic Advantages:
- Reduced Reliance on Imports: Pakistan’s dependence on imported fossil fuels strains its foreign exchange reserves. Solar power, being indigenous, lessens this dependence, freeing up valuable resources.
- Long-Term Cost Savings: While the upfront cost of solar panels exists, they require minimal maintenance and boast a lifespan of 25-30 years. This translates to significant savings on electricity bills in the long run, especially with rising fossil fuel prices.
- Economic Growth: The burgeoning solar industry creates new job opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance, fostering economic development and empowering local communities.
- Grid Stability: Distributed solar power generation reduces the burden on the national grid, lowers transmission losses, and enhances overall grid stability.
Addressing Affordability:
The initial cost can be a barrier for some. However, initiatives are mitigating this challenge:
- Government Incentives: Subsidies, tax breaks, and streamlined regulations promote solar adoption.
- Financing Schemes: Soft loans from institutions like the State Bank of Pakistan make solar solutions more accessible.
Cost-Effective Solutions:
Three main solar system types cater to diverse needs and budgets:
- On-Grid Systems: Ideal for locations with consistent grid availability and individuals aiming to primarily reduce electricity bills.
- Cost: Most economical due to the absence of battery storage.
- Functionality: Generates electricity during the day, feeding it directly into the grid.
- Off-Grid Systems: Ideal for remote areas with no grid access or frequent outages.
- Cost: Moderately priced compared to hybrid systems. Battery addition increases the cost.
- Functionality: Generates and stores electricity for later use.
- Hybrid Systems: Ideal for locations with inconsistent grid supply or those seeking complete energy independence.
- Cost: Most expensive due to battery inclusion (tubular or lithium).
- Functionality: Operates similarly to on-grid systems but provides backup power during outages.
Choosing the Right System:
- On-grid: Prioritize if you have a reliable grid and aim to reduce electricity bills.
- Off-grid: Opt for this if you lack grid access or experience frequent power cuts.
- Hybrid: Consider this if you experience outages and require backup power, but be prepared for a higher investment.
Additional Considerations:
- Battery technology: Tubular batteries are cheaper but have a shorter lifespan. Lithium batteries offer a longer life cycle and better performance but are more expensive.
- Government incentives: Explore available subsidies and tax breaks to enhance affordability.
The Road Ahead:
Embracing solar energy presents a win-win scenario for Pakistan. It lessens the nation’s reliance on expensive imports, fosters economic growth, and paves the way for a sustainable future.
Call to Action:
- Government: Continued policy support through further incentives, streamlining regulations, and promoting research and development is crucial.
- Financial Institutions: Offering innovative financing solutions can incentivize wider adoption.
- Individuals and Businesses: Investing in solar solutions not only benefits your wallet but also contributes to a cleaner and more secure energy future for Pakistan.
By prioritizing solar energy, Pakistan can illuminate a path towards a brighter economic and environmental future.